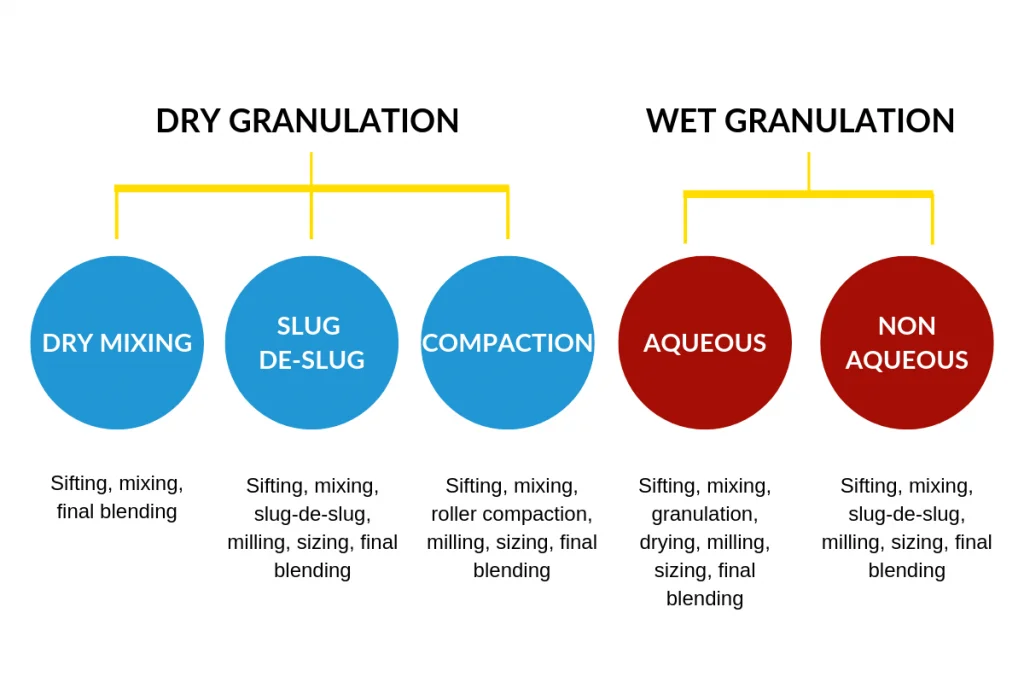
The choice of granulation technique (wet, dry, or direct compression) for a drug product depends on various factors, including the drug’s stability, solubility, desired release profile, physical properties, chemical properties and manufacturing considerations. Wet granulation is suitable for moisture-stable drugs and fluffy materials with low bulk density, while dry granulation is preferred for moisture-sensitive and heat-sensitive drugs and direct compression is suitable for the materials which have superior flow and compressibility.
Wet granulation:
Wet granulation is a process that produces granules from a powder mixture by adding a liquid binder and then agitating the mixture. This process is commonly used to improve the flowability, compressibility, and uniformity of powders.
Wet granulation is the most common granulation technique used in the pharmaceutical industry.
During the wet granulation process, so many stages are involved like sieving, binder preparation, granulation, drying, milling, screening, blending and lubrication.
Based on the nature of the active pharmaceutical ingredient and its sensitivity, granulating fluids can be selected either individually or in combination, like water, isopropyl alcohol, ethanol, and dichloromethane.
Advantages of Wet Granulation Technique:
- · It improves the drug uniformity.
- · It gives better compressibility and flowability.
- · Improves the dissolution rate of drug products.
- · Reduces the dust formation and risk of contamination.
- · Suitable for high-dose drugs and APIs with poor flow
Disadvantages of Wet Granulation Technique:
- · It is a complex process and involves multiple stages.
- · Required specialized equipment and more manpower.
- · Not suitable for moisture and heat-sensitive materials.
Dry Granulation:
Dry granulation is the method of forming granules by applying pressure or shear force to the dry powder without using a liquid binder solution. This technique is suitable for moisture and heat-sensitive drugs.
During the dry granulation process, so many stages are involved like sieving, blending, compaction, milling, screening, blending and lubrication.
Advantages of Dry Granulation:
- · Suitable for moisture-sensitive or heat-sensitive active pharmaceutical ingredients.
- · Improves the chemical stability.
- · Cost-effective compared with wet granulation.
Disadvantages of Dry Granulation
- · This process generates more dust and it may lead to process loss.
- · It required specialized equipment (Roller Compactor) and skilled manpower.
- · To get the desired percentage of granules, it will take much time.
Direct compression:
Direct compression is a tablet manufacturing technique where the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and excipients are directly blended and compressed into tablets without any additional processing steps like granulation.
Advantages of Direct compression:
- · It is a cost-effective process and requires less manpower.
- · Involves only a few stages of the process and requires less equipment.
- · It reduces the risk of contamination.
- · Active pharmaceuticals with better flowability will be suitable for this technique.
Disadvantages of Direct compression:
- · High-dose drugs with low bulk density may not be suitable for this process.
- · Required specialized excipients to improve the flowability and compressibility.
- · Uniform blending can be difficult with low-potency drugs.
- · Direct compression can be prone to sticking, picking, capping and lamination.
At Sands Active (PVT.) LTD., we have state-of-the-art R&D and manufacturing facilities. We will evaluate the active pharmaceutical ingredients prior to the initiation of development activity and understand the API’s physical and chemical properties. Based on the evaluation, we will finalize the right granulation technique and validate the manufacturing process to enhance the quality of product for the customers.